| Meeting Brochure and registration form SMDM Homepage | |
|

|
|
||||
Purpose: The global effort to scale-up HIV antiretroviral treatment (ART) poses tremendous logistical challenges for resource-limited countries. Working with a major NGO providing technical assistance to such countries, we are developing a decision support tool for evaluating treatment capacity in specific resource-limited environments.
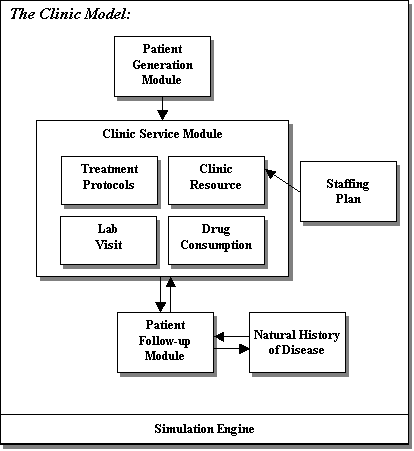
Methods: We created a discrete-event simulation model designed to capture patient flow time, waiting time, clinic parameters, and competition for limited treatment resources in an HIV ART clinic in resource-limited settings. The model, created on a standard industrial DES platform, simulates a variety of clinical details including patients' disease stage, physiological reactions to treatment, clinic services, lab tests, and demand for drugs. The simulation module runs on top of a relational database storing demographic information and resource related data. Model outputs, which are written to the database, include treatment capacity, health resource (workforce and material) utilization at different levels of coverage, patient eligibility, and other parameter values.
Results: Output of the model includes resource utilization for medical workforce and facility. The model predicts treatment capacity for a given clinic size, staffing plan, and treatment protocol. The model also suggests a timeline for scaling up the number of clinics required to accommodate additional demand over time. We are implementing additional modules for laboratory usage and drug demand.
Conclusion: This tool can be used to support local planning for HIV ART clinics, including issues of staffing, resource allocation, and operational decisions such as admission policies. At the regional or national level, it may be used to forecast demand for healthcare workers and ART drugs, given the target treatment population, regional demographics, and treatment protocols.
 |
See more of Poster Session III
See more of The 28th Annual Meeting of the Society for Medical Decision Making (October 15-18, 2006)