|
||||
Sunday, October 21, 2007
P1-29
PREDICTING EQ-5D-US HEALTH STATE VALUES FROM THE OSTEOPOROSIS ASSESSMENT QUESTIONNAIRE
Methods: EQ-5D-US and OPAQ data were collected from individuals at two centers who had experienced osteoporosis-related fracture. Fractures were classified by type as hip, vertebral, wrist, “like a hip,” “like a wrist,” “like a vertebral,” or “like a finger/toe.” Spearman rank correlations between EQ-5D attributes (mobility, pain, activity, self-care, anxiety) and OPAQ subscales (physical function, emotional status, social interaction, and symptoms) were estimated. Linear regression was used to estimate EQ-5D health state values based on OPAQ subscales, age, sex, and fracture type.
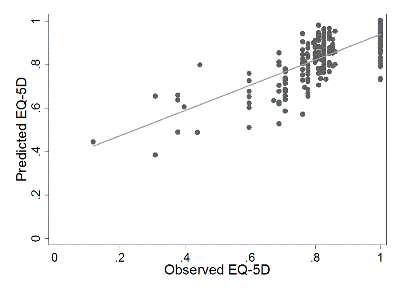
Results: A total of 283 participants (79 men and 204 women), mean age 67 (range 50-89), completed both EQ-5D and OPAQ. The distribution of fractures types was 10% hip, 18% vertebral, 24% wrist, 5% "like a hip", 11% "like a vertebral", 18% "like a wrist" and 13% "like a finger/toe". Statistically significant correlations were observed for all EQ-5D attributes and three of the four OPAQ subscales (all except social interaction). The final regression model, which included age, sex, fracture type and three OPAQ attributes (physical function, emotional status and symptoms) predicted 58% of the variance in EQ-5D-US scores. The figure shows a plot of observed versus predicted values.
Conclusion: Estimation of EQ-5D-US health state values from OPAQ may facilitate cost-effectiveness analyses in trials where OPAQ is used.